What is Azure Blob Storage?

Azure Blob Storage is Microsoft’s cloud-based object storage service for storing massive amounts of unstructured data - such as images, videos, documents, backups, and logs. The term “blob” stands for Binary Large Object, meaning it can store virtually any file format without a fixed structure.
It is designed for high availability, global accessibility, and cost efficiency, making it a preferred choice for businesses and developers needing scalable cloud storage.
What is it Used For?
Azure Blob Storage is suitable for various scenarios:
-
Media hosting for websites or streaming platforms.
-
Backup and disaster recovery storage.
-
Big data analytics (data lakes).
-
Archiving compliance or historical records.
-
IoT data storage from sensors and devices.
-
Static web content hosting like CSS, JavaScript, and images.
Blob Types
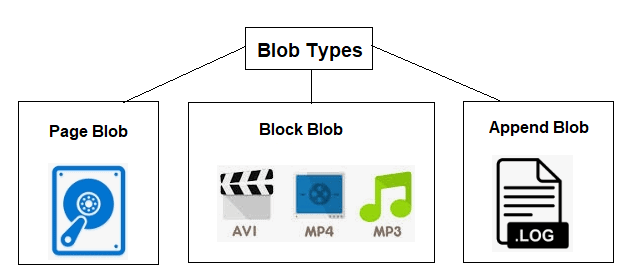
Before talking about tiers, it’s important to understand the three blob types supported in Azure:
Block Blobs
-
Store text or binary data in blocks.
-
Ideal for media files, documents, and backups.
-
Optimized for uploading large files efficiently.
Append Blobs
-
Designed for append-only operations.
-
Great for logging scenarios where data is continuously added.
Page Blobs
-
Store random-access files like Virtual Hard Disk (VHD) files.
-
Used mainly in Azure Virtual Machines.
Blob Storage Tiers

Azure Blob Storage tiers let you choose the most cost-effective way to store your data based on how often it’s accessed and how quickly you need it.
1. Hot Tier
-
Purpose: For data that is accessed or modified frequently.
-
Cost: Highest storage cost, but lowest access/read cost.
-
Retrieval Time: Instant access.
-
Example Use Case: Website images, real-time analytics data, active project files.
🔥 Tip: If your files are being read multiple times a day, the Hot tier is more cost-efficient despite the higher storage price.
2. Cool Tier
-
Purpose: For data accessed less frequently but still needed without delay.
-
Cost: Lower storage cost than Hot, but higher access/read cost.
-
Retrieval Time: Instant access.
-
Example Use Case: Monthly reports, seasonal marketing assets, short-term backups.
🧊 Tip: Cool tier saves money for data you might open only a few times per month, but remember that frequent access can make it more expensive than Hot in the long run.
3. Archive Tier
-
Purpose: For rarely accessed data that can wait hours to retrieve.
-
Cost: Lowest storage cost, highest access/read cost, plus retrieval fees.
-
Retrieval Time: Several hours.
-
Example Use Case: Long-term compliance data, historical logs, disaster recovery backups.
🗃️ Tip: Archive is excellent for cold storage, but retrieval time can take 15+ hours depending on size and settings.
Conclusion
Azure Blob Storage gives you flexibility in storage types and cost models. By understanding blob types (Block, Append, Page) and access tiers (Hot, Cool, Archive), you can optimize performance and save money. The key is to analyze your data access patterns and match them to the correct tier.
